Study finds nanoparticles in over one-quarter of foodstuffs
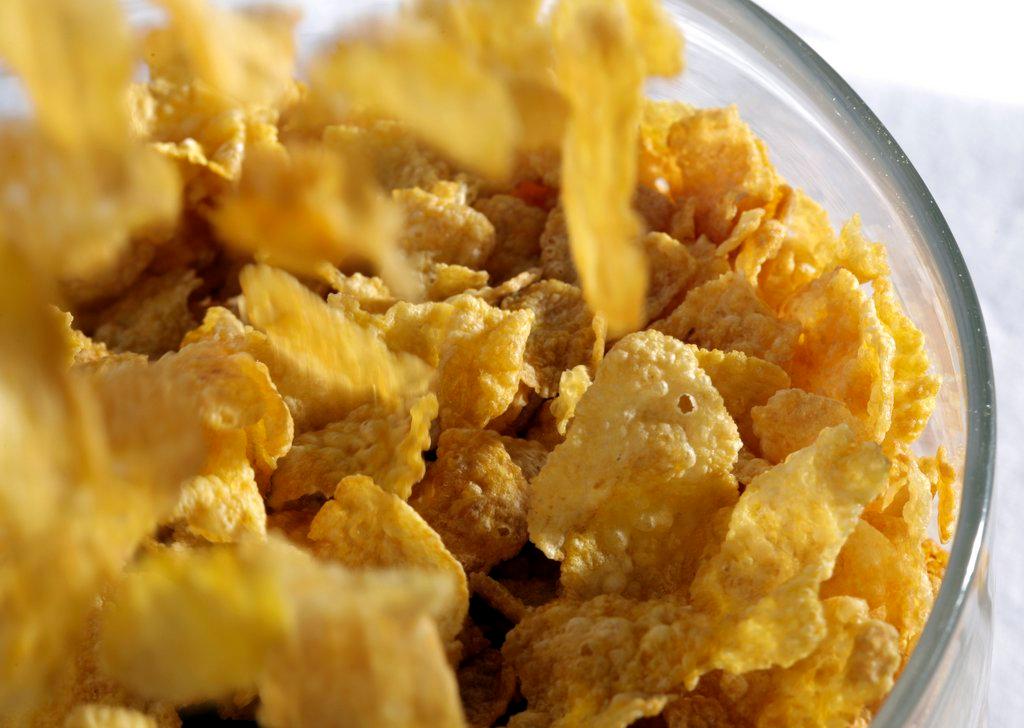

Nanoparticles were found in over one quarter of foodstuffs - as additives and colourings - tested in a pilot study carried out in French-speaking Switzerland. The potential health risks of such particles have still not been fully evaluated.
Tests revealed the presence of nanoparticles in 27% of food products, or 15 out of 56 samples, according to a study released on Tuesday by cantonal chemists in French-speaking Switzerland, in collaboration with the Adolphe Merkle Institute of the University of Fribourg and the Federal Food Safety and Veterinary Office (FSVO).
Nanoparticles are smaller than 100 nanometres in size. One nanometre is around one millionth the diameter of a pinhead.
Three nanoparticles were tested: titanium oxide (TiO2), silicon oxide (SiO2) and talc. In Switzerland, they are known as the food additives and colourings, E551 and E171. While they are often declared on food packaging, generally it is not specified that they are present in the form of nanoparticles.
The foods tested were mainly sauces, biscuits or breakfast cereals. All 5 chewing gum samples contained either titanium or talcum oxide.
The new food law, which came into force in Switzerland on May 1, 2017, obliges manufacturers to declare nanomaterials on labelling, such as on packaged food. Firms have four years to ensure they are compliant with the law.
The cantonal chemists who took part in the study warned that nanoparticles’ effects are still poorly understood and that the health risks associated with their ingestion by the human body remain very hard to assess.
“There are still studies to be done. Nanoparticles also exist in nature, which does not mean that their industrial counterparts are free from any danger,” Geneva-based chemist Patrick Edder told Keystone-ATS.
The FSVO, for its part, said nanoparticles “can have effects on the cardiovascular system or other organs. Whether or not they are toxic depends on the material and dosage”. But it said silicon or titanium oxide did not present any health-endangering toxicity, and that an authorisation is required for any new nanomaterial.

In compliance with the JTI standards
More: SWI swissinfo.ch certified by the Journalism Trust Initiative


You can find an overview of ongoing debates with our journalists here. Please join us!
If you want to start a conversation about a topic raised in this article or want to report factual errors, email us at english@swissinfo.ch.