
Swiss ban widely-used pesticide over health and environment fears
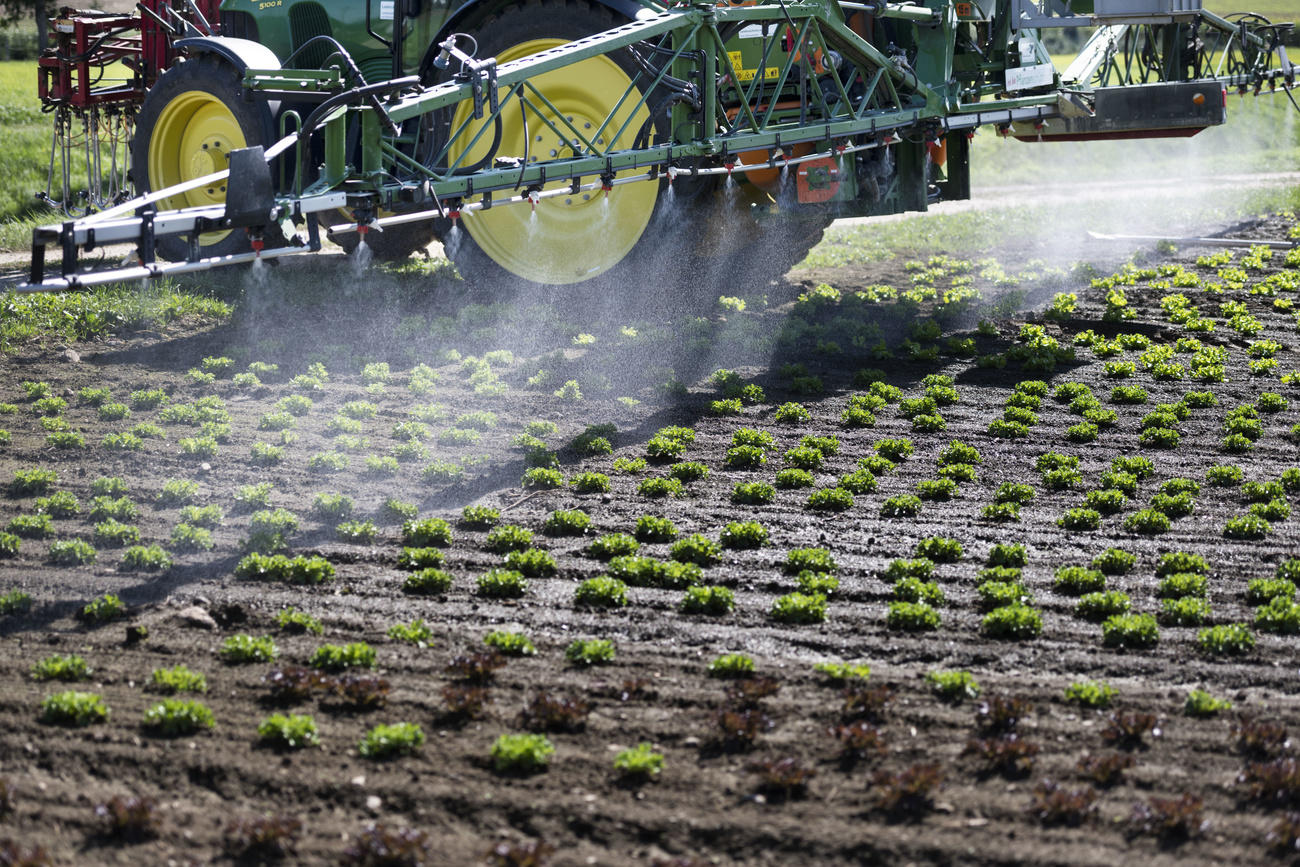

The Federal Office for Agriculture has banned chlorothalonil, a fungicide used since 1970s to prevent mildew and mould on crops.
The federal office said on ThursdayExternal link that it had decided to withdraw the sales authorisation for products containing chlorothalonil with immediate effect.
The ban occurred amid an ongoing review of 100 substances, the agriculture office said.
New laboratory results had been provided by firms indicating the toxicity of certain chlorothalonil by-products.
The office said: “It is not possible to exclude that some chlorothalonil by-products do not have a long-term negative effect on health.”
The agriculture office supports the EU Commission’s assessment that chlorothalonil should be classified as a carcinogen. According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), chlorothalonil is especially toxic to fish and aquatic invertebrates. Exposure to the agent can cause kidney and stomach damage, including tumours, in rodents. A ban on the substance will take effect in the European Union in 2020, following conclusions from the European Food Safety Authority that the agent could pose a health risk.
Drinking water risk
Swiss officials said it was important to “act quickly” to reduce the presence of chlorothalonil by-products in groundwater, as they may exist at levels above legal standards set for drinking water in Switzerland.
Last June drinking water in a village in canton Fribourg had to be cut after excessive amounts of chlorothalonil were discovered.
The Swiss authorities say the requirements for approval of plant protection products have been tightened in recent years. They say products that were eligible for approval 20 years ago are not necessarily the same today. The pesticide approval process in Switzerland is currently being reviewed by an external audit firm.
The government is taking measures against contaminated drinking water with its action plan to reduce pesticide pollution and the Agricultural Policy 22+, but critics say these do not go far enough. Two popular initiatives on drinking water are pending. Although the government has rejected these, voters are likely to have the final say next year.

More
Pesticide companies ‘seriously deficient’ on human rights, says UN toxics expert

In compliance with the JTI standards
More: SWI swissinfo.ch certified by the Journalism Trust Initiative




























You can find an overview of ongoing debates with our journalists here . Please join us!
If you want to start a conversation about a topic raised in this article or want to report factual errors, email us at english@swissinfo.ch.