
New ultrasound technique improves breast cancer detection
Zurich-based researchers have developed an ultrasound technique that can help distinguish benign breast tumours from malignant ones.
An ultrasound probe emits sound waves that penetrate the body. Because organs and tissues have different physical properties, they reflect the waves differently. The device analyses these “echoes” and reconstructs a three-dimensional image of the inside of the body called an “echograph”, or more commonly, ultrasound.
Usually, the device measures the intensity of the reflected sound waves. But a team from the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology ETH Zurich also studied the echo duration, which allowed them to produce images with enhanced contrast that are useful for cancer diagnosis. The researchers were thus able to detect the presence of tumours and distinguish benign tumours from malignant ones.
The density and rigidity of body tissues determines the speed of the sound echo. Tumours are more rigid than the surrounding tissue, especially when they are cancerous. As a result, sound travels 3% faster on average in malignant tissues than in healthy tissues, and 1.5% faster than in benign tumours.
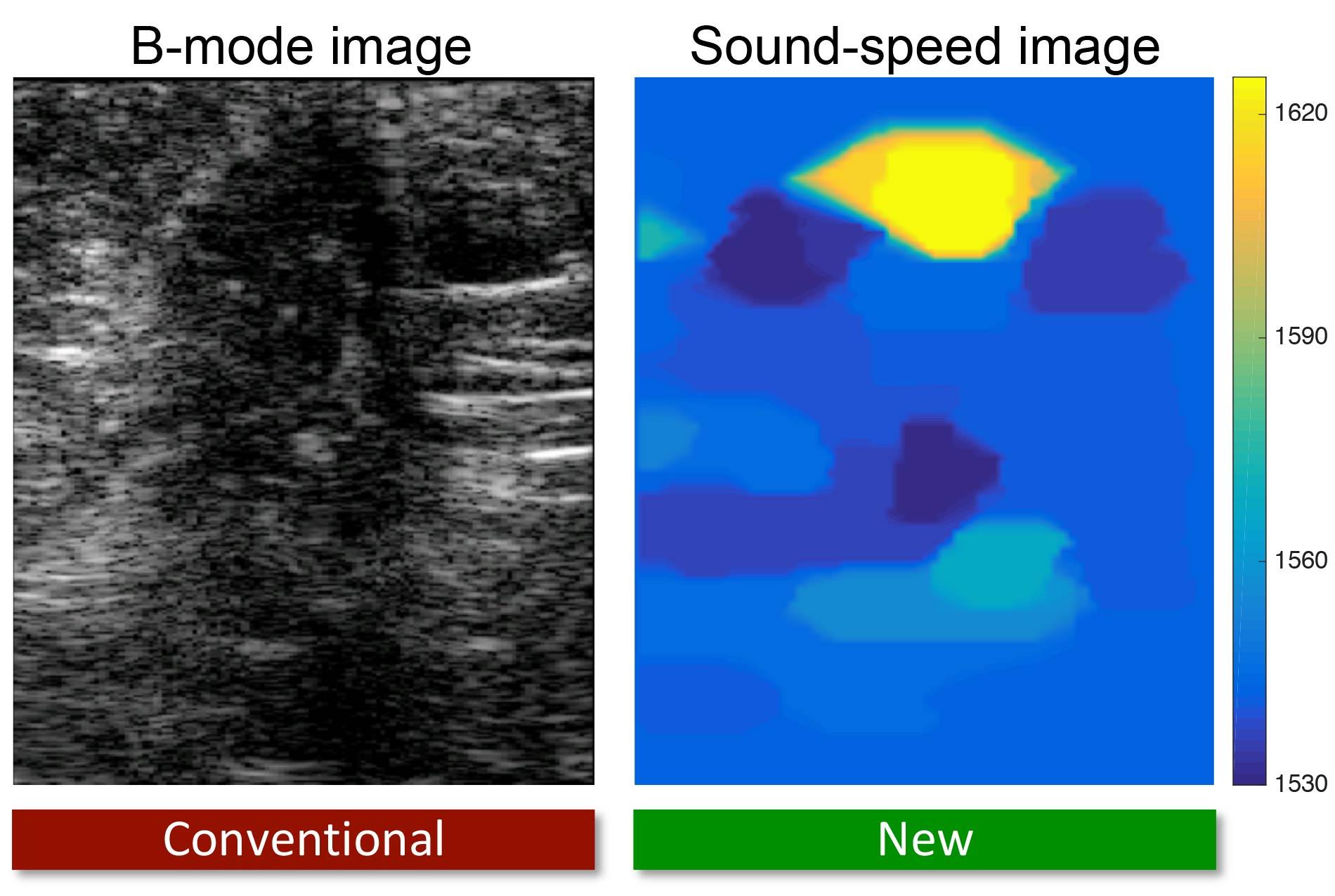

During clinical trials, which are ongoing, the Zurich team demonstrated the effectiveness of their prototype in detecting breast tumours.
“Our goal is to provide physicians with a better tool for decision-making during routine checks, and to avoid unnecessary biopsies,” said Orçun Göksel, assistant professor at ETH Zurich and director of the study. “Compared with conventional ultrasound, our images are much easier to interpret.”
Their work, which was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF), has been published in the journal Physics in Medicine and BiologyExternal link.

In compliance with the JTI standards
More: SWI swissinfo.ch certified by the Journalism Trust Initiative






























You can find an overview of ongoing debates with our journalists here . Please join us!
If you want to start a conversation about a topic raised in this article or want to report factual errors, email us at english@swissinfo.ch.