
Invasive quagga mussel could profoundly change Swiss lakes
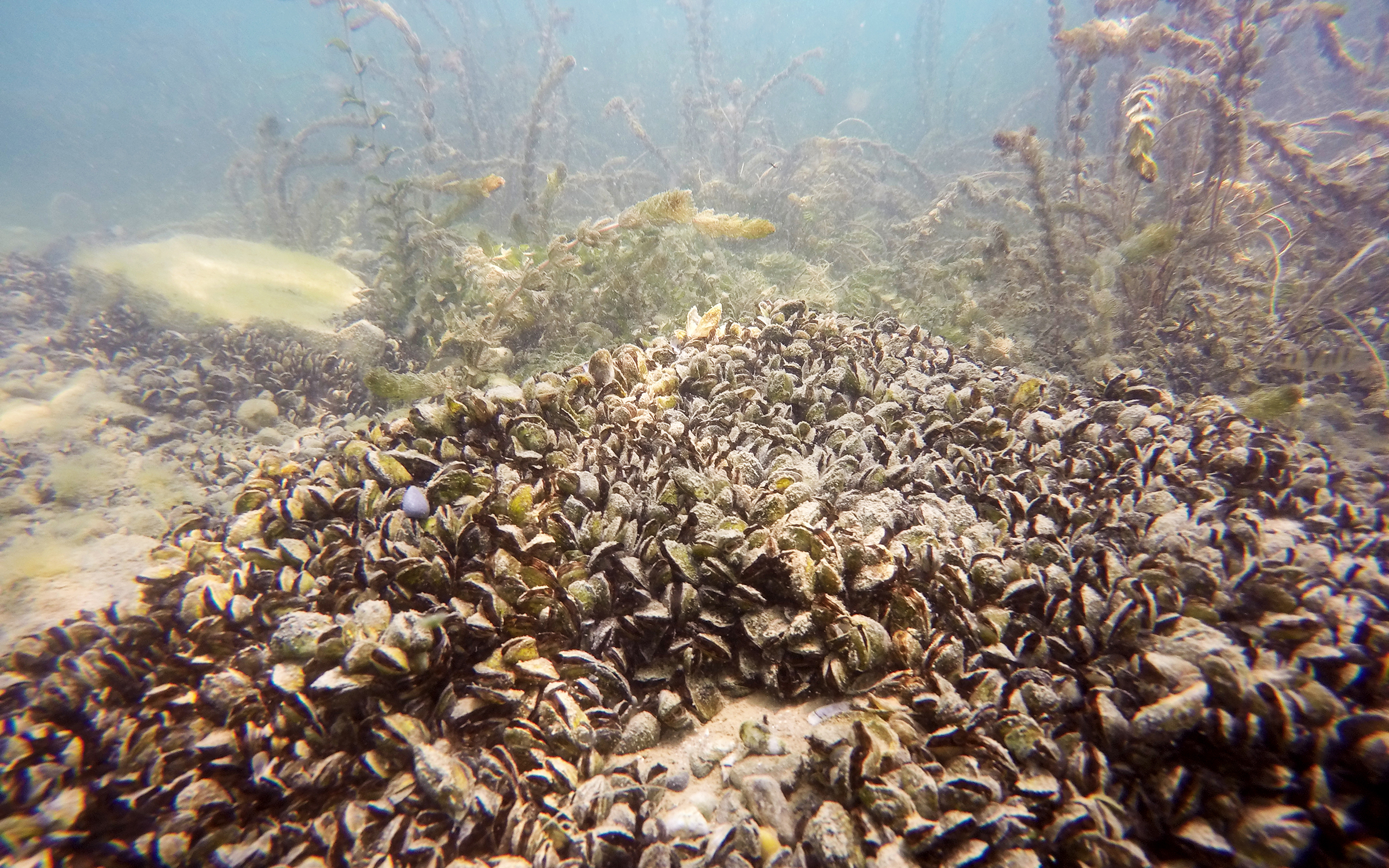

The quagga mussel, originally from the Black Sea region, is spreading rapidly in Swiss lakes. Experts fear that the invasive species could upset lake ecosystems.
The quagga mussel (Dreissena bugensis) was first discovered in 2014 in the River Rhine near Basel. Since then, it has spread rapidly and already colonised numerous lakes in Switzerland, namely Lake Constance, Lake Geneva, Lake Neuchâtel, Lake Biel, Lake Murten and Lake Hongrin (near Lake Geneva), the Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology (EAWAG) said in a statementExternal link on Thursday.

Together with the zebra mussel, which has been spreading in Swiss lakes since the 1960s, the quagga mussel is one of the most aggressive invasive species.
The quagga mussel is able to reproduce almost all year round and can inhabit the soft substrate in deep-water zones. These characteristics, together with the fact that it is more efficient at absorbing nutrients, are considered to be the main reasons why the quagga out-competes the zebra mussel in deep-water lakes, and why it is increasingly crowding it out, EAWAG said.
The mussels spread either naturally by floating in the current in their larval state and being carried downstream, or by being transported unintentionally by humans in the ballast, bilge or engine-cooling water of boats and leisure craft. In addition, the adult mussels stick firmly to boats and other objects, and if these are not cleaned or properly dried before being moved to different lakes, the mussels can spread in this way, too.
‘Far-reaching consequences’
“On the basis of observations that we have from North America, we fear that the presence of the quagga mussel will have far-reaching consequences for our lakes’ ecosystems, the balance of which could potentially be upset,” said EAWAG researcher Piet Spaak, head of the SeeWandel projectExternal link, which involves seven research institutions in Germany, Austria and Switzerland. They are investigating the complex interplay between nutrient depletion, climate change, invasive and non-native species and other stress factors.
Although detailed consequences are as yet unknown, they could include a reduction in plankton, as the mussels filter large volumes of phytoplankton, a reduction in fish stock due to an altered food web, mussel shells in shore areas and increased maintenance and costs, for example for boats, pipes and fishing nets.

More
The Swiss Alps are beautiful, but are they biodiverse?

In compliance with the JTI standards
More: SWI swissinfo.ch certified by the Journalism Trust Initiative





























You can find an overview of ongoing debates with our journalists here . Please join us!
If you want to start a conversation about a topic raised in this article or want to report factual errors, email us at english@swissinfo.ch.