
Artificial intelligence used to detect plastic waste at sea
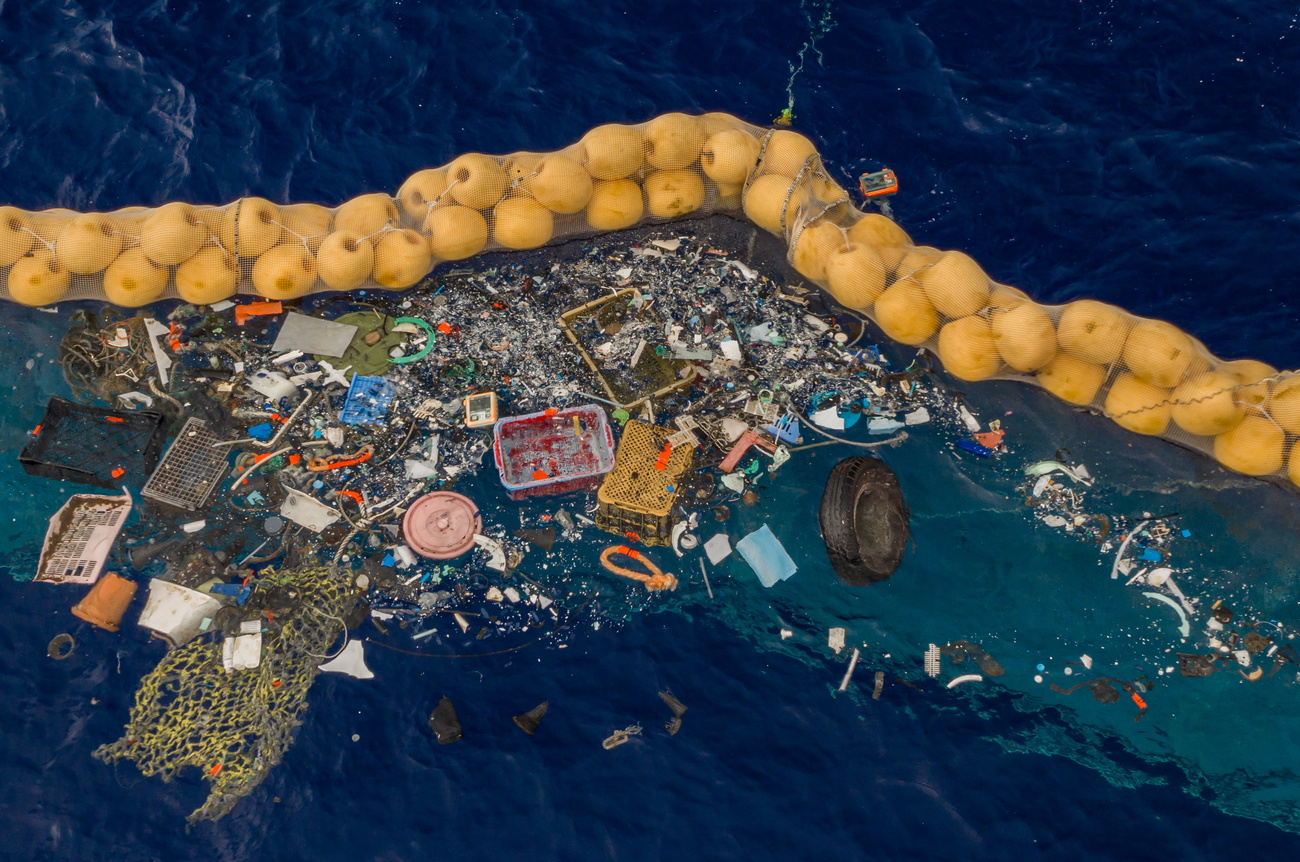

Scientists at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Lausanne (EPFL) and Wageningen University in the Netherlands have developed an artificial intelligence (AI) model that recognises plastic objects floating on the water in satellite images. This could make it possible to eliminate this waste using ships.
The accumulation of waste at sea is certainly visible on Sentinel 2 satellite images from the European Space Agency (ESA). But since we are talking about terabytes of data, they need to be analysed automatically using AI models, EPFL said in a press release on Thursday.
Scientists have developed an AI-based detector that estimates the probability of the presence of marine debris for each pixel of Sentinel-2 satellite images. The detector remains accurate even in difficult conditions, such as when cloud cover and haze prevent existing models from accurately identifying debris.
+ Plastic entering oceans could nearly triple by 2040 if left unchecked -research
In addition to more accurate prediction of marine debris aggregations, the detection model also makes it possible to identify debris in PlanetScope images from nanosatellites, which are accessible on a daily basis. The combination of Sentinel-2’s weekly acquisitions and PlanetScope’s daily acquisitions can bridge the gap towards continuous daily monitoring, according to the authors.
PlanetScope and Sentinel-2 sometimes capture the same area of marine debris on the same day, just a few minutes apart. This double view of the same object in two locations reveals the direction of drift due to wind and ocean currents. This information can be used to improve models for estimating the drift of marine debris.
+ Switzerland has plastic problem, say most Swiss
Wageningen University will continue these explorations in collaboration with partners in the Netherlands, such as Ocean Cleanup, which collect plastic on the high seas using specialised vessels.
This research stems from the ADOPT (AI for Detection of Plastics with Tracking) project, carried out in collaboration with the Swiss Data Science Center, a joint venture between EPFL and the federal technology institute ETH Zurich. The research is published in the journal Cell iScience.
This news story has been written and carefully fact-checked by an external editorial team. At SWI swissinfo.ch we select the most relevant news for an international audience and use automatic translation tools such as DeepL to translate it into English. Providing you with automatically translated news gives us the time to write more in-depth articles. You can find them here.
If you want to know more about how we work, have a look here, and if you have feedback on this news story please write to english@swissinfo.ch.

In compliance with the JTI standards
More: SWI swissinfo.ch certified by the Journalism Trust Initiative





























You can find an overview of ongoing debates with our journalists here . Please join us!
If you want to start a conversation about a topic raised in this article or want to report factual errors, email us at english@swissinfo.ch.