In space exploration, Switzerland punches above its weight
A double Nobel Prize and instruments on board 50 European, American, Russian and Chinese missions. In space, Switzerland is everywhere. It will charter the first ‘garbage truck’ in earth orbit, it has its own telescope for exoplanets (Cheops) and its technology is also present on the fabulous James Webb Space Telescope.
Its images are still amazing the world. Because it looks into the infrared, is much larger than the Hubble, and is not positioned in low orbit, the James Webb telescope is the most powerful astronomical instrument ever built by mankind. And among its builders, there are also Swiss.

More
A glimpse into the origins of the universe
The announcement by the European Space Agency in December 2020 was a momentous one for the Swiss space community. The agency had agreed to allocate almost CHF100 million to ClearSpace-1, an initiative/start-up by Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Lausanne (EPFL) to clear space debris.
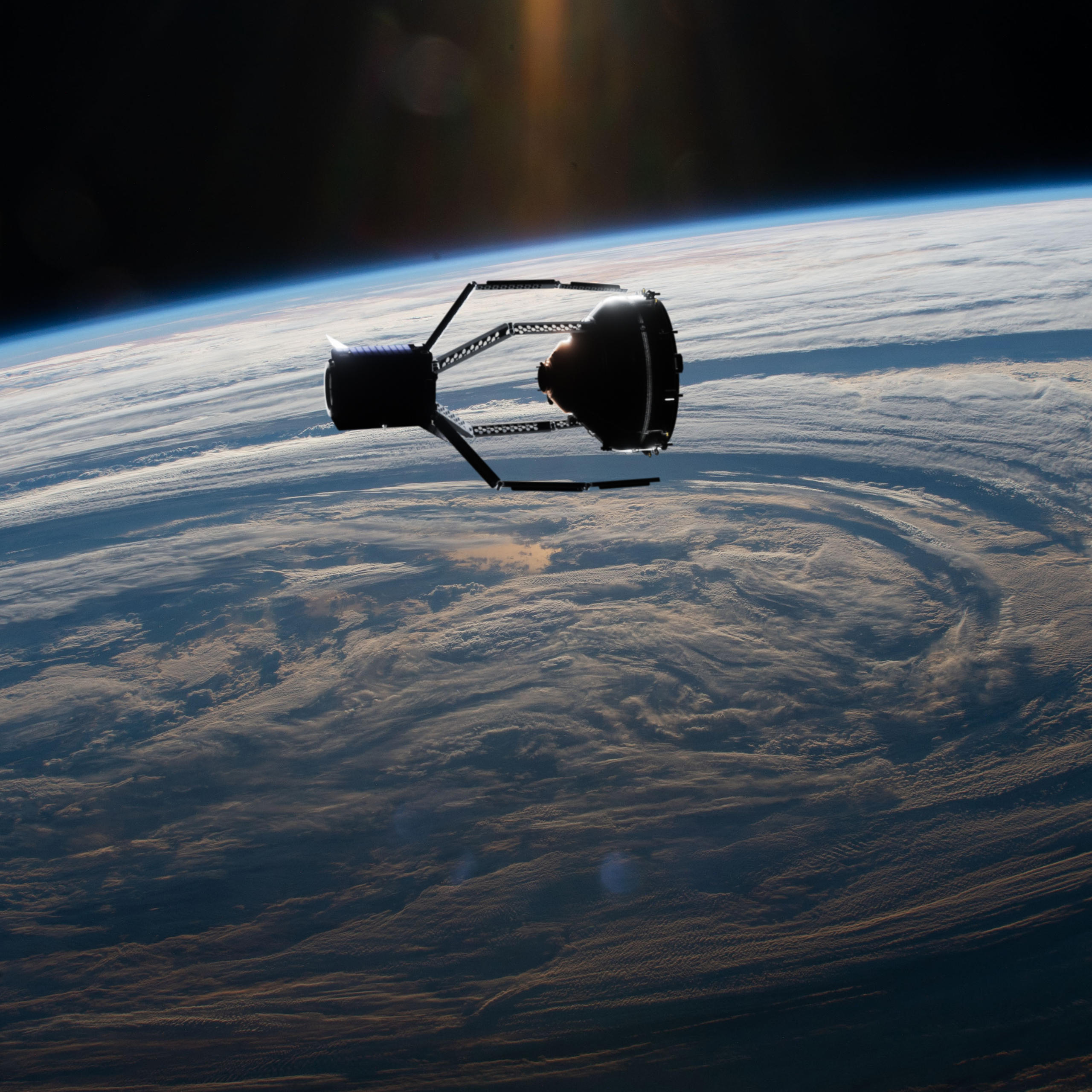

More
The world’s first space ‘garbage truck’ will be Swiss
Swiss scientists and engineers have built their reputation in space exploration and research over many years.
A discovery in 1995 made little noise outside scientific circles. But as the years passed, the public began to realise that what was once the realm of science fiction had become a proven reality: the galaxy is teaming not only with stars, but also with planets. The first to have identified one of these planets orbiting a star other than our sun were none other than Switzerland’s own Michel Mayor and Didier Queloz.
And 24 years later, the discovery earned Mayor and Queloz the Nobel Prize for physics.
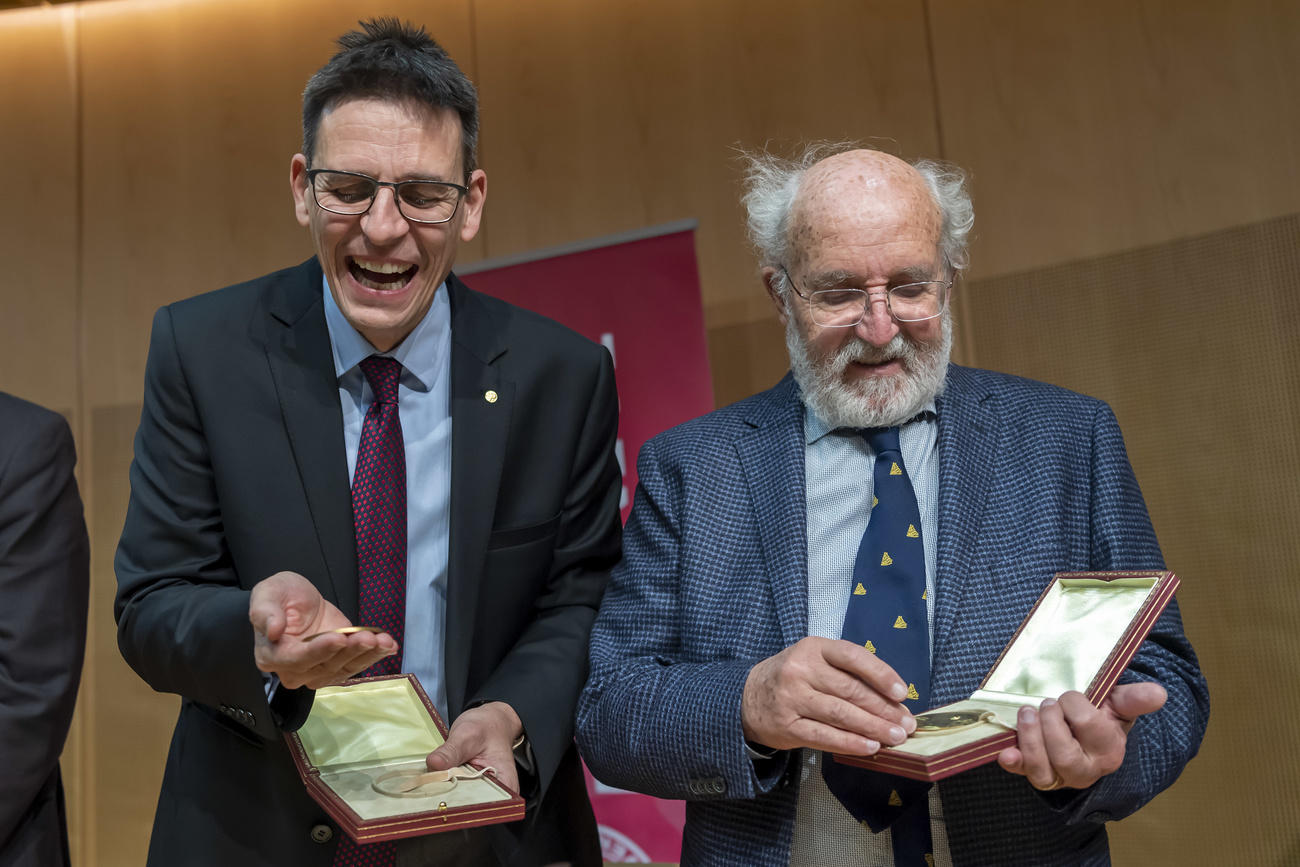

More
‘With the Nobel Prize, you’ve reached the Olympus of science’
Excitement aside, the Nobel Prize is certainly justified. The discovery was one of the most important in astronomy in the 20th century. It opened new fields of research for understanding our place in the universe and it multiplied by millions the chances of finding extra-terrestrial life.

More
Thousands of planets – but is there life out there?
But the search for other lifeforms is not an easy task when we are looking for it on distant worlds that are hundreds of thousands of billons of kilometres away. This is where human ingeniousness intervenes. And here also, is where the Swiss are present.
Ingenuity was required from the very outset of this quest. But how is it, in fact, that we are sure of the existence of these planets when, apart from on one or two grainy photographs of vague spots of light, no one has ever seen them?
But it might not be necessary to explore planets that far away. Bern-based scientists hope to find life in space using a state-of-the art instrument known as ORIGIN that may be used on future space missions to Jupiter and Saturn.
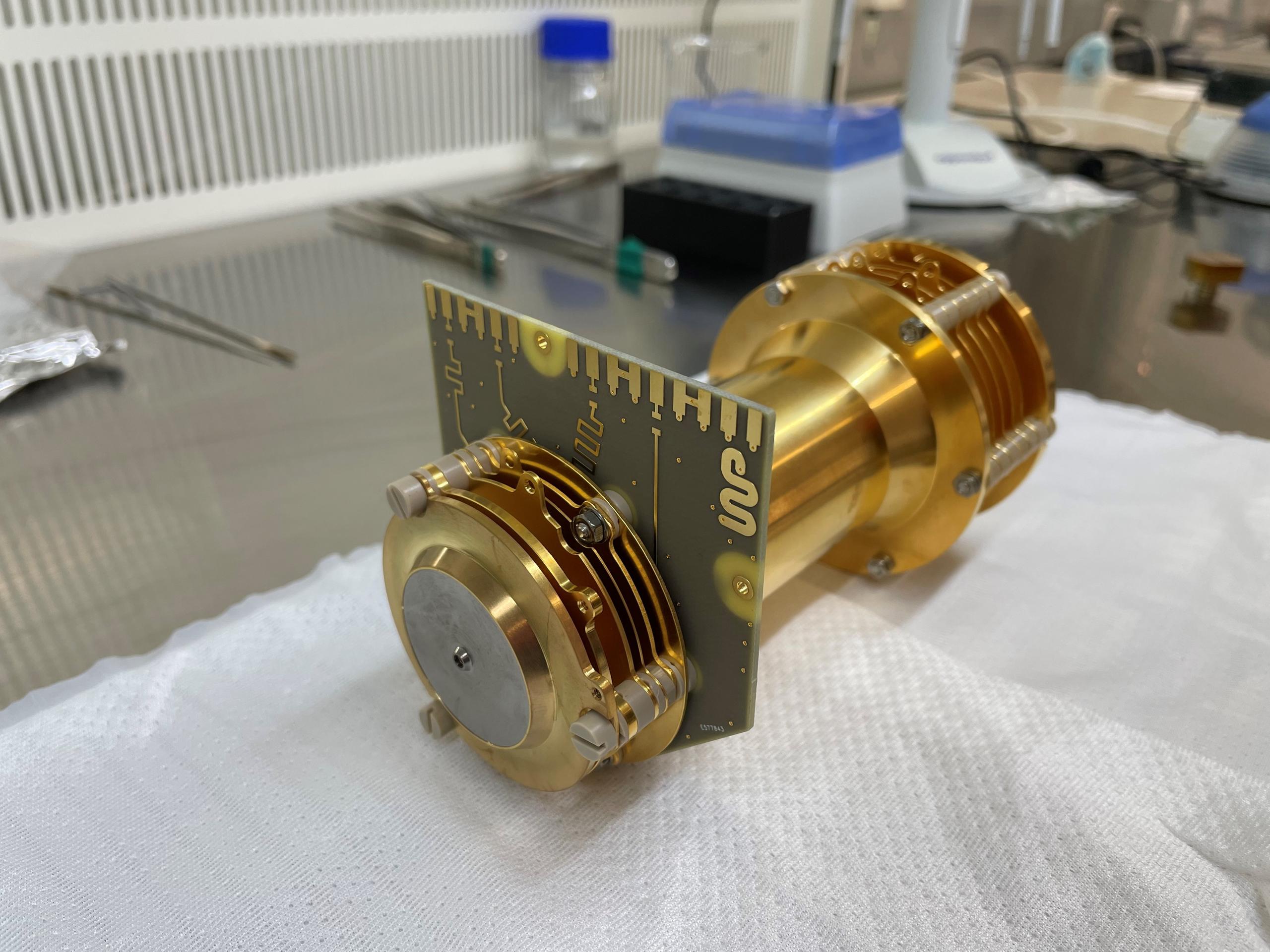
More
Bern scientists hope to find the building blocks of life in space

More
Billions of worlds to discover
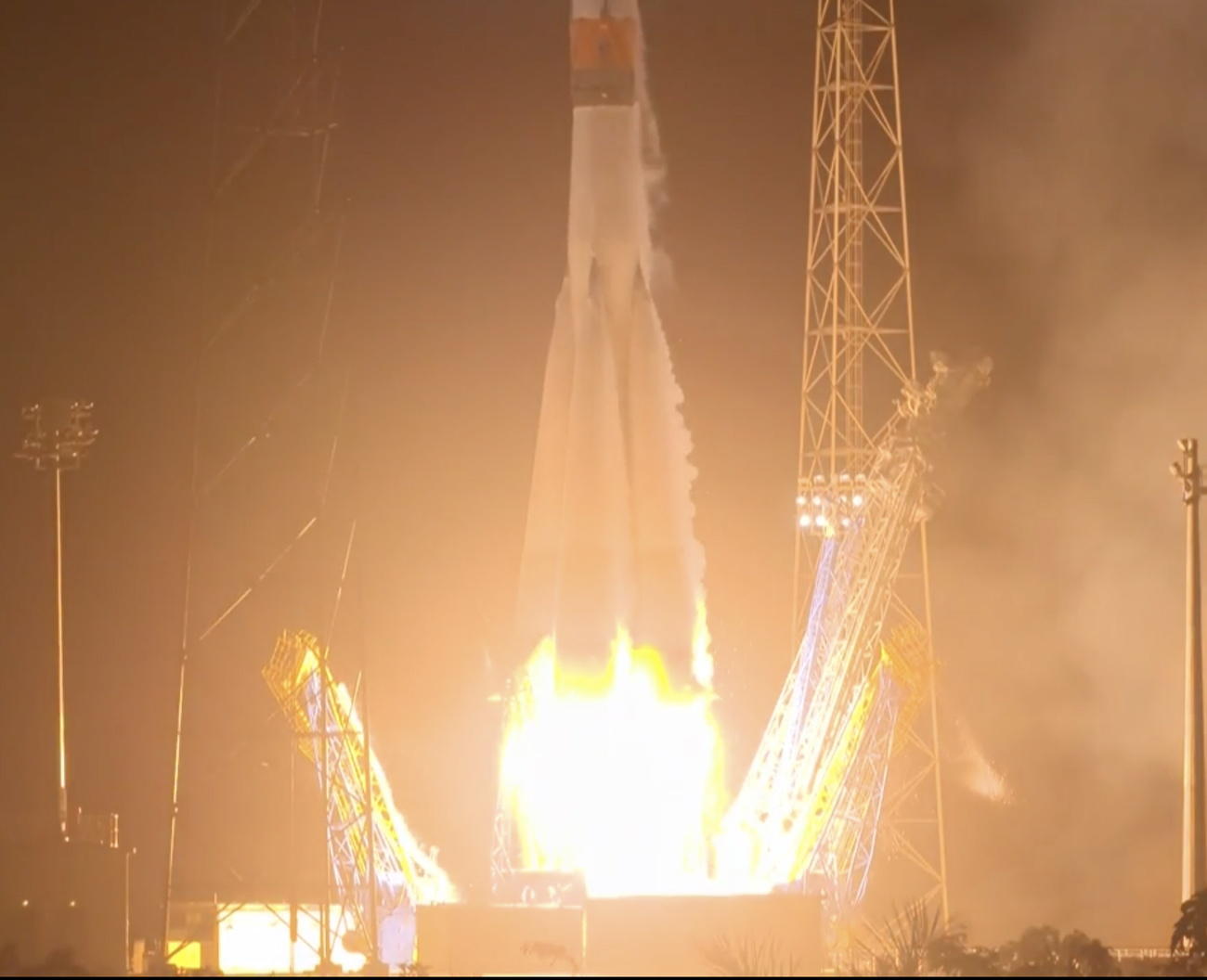
Meanwhile, research into exoplanets continues. Today scientists have the instruments and technology to better understand what such distant planets are made of. This is the mission of the CHEOPS spatial telescope, the first European satellite ‘Made in Switzerland’ that was launched in December 2019.

More
Swiss-developed exoplanet telescope launched into space
But the Swiss reputation in space exploration was not established with CHEOPS, neither with Mayor and Queloz, nor even with the Swiss astronaut Claude Nicollier – first non-American mission specialist at NASA.
In 1969, Armstrong and Aldrin landed on the moon wearing Swiss watches on their wrists. And the first thing they did upon arrival, even before unfurling the star-spangled banner, was to install a solar sail from the University of Bern, itself being the only non-American scientific experiment on board Apollo 11.

More
The beautiful lunar toy from Bern
Since the beginning of space exploration, there has hardly been an American or European mission which did not include Swiss technology. That’s because this country knows how to make instruments which are both very precise and very reliable, indispensable attributes for responding to the constraints of a space voyage.
Whether it is propelling a rover on Mars, ‘sniffing’ the gas which escapes from a comet or taking high definition images of a planet in the solar system, Swiss engineers have the solution.
The most recent example: STIX. This X-ray telescope will study solar eruptions from a European probe which will approach closer to the Sun than anything that has been attempted before.

More
Solar Orbiter blasts off with Swiss telescope on board
Switzerland, country of watchmaking and precision mechanics also has highly advanced education and research support systems, which explains in part how a small country in the mountains has become a big country in space.

More
Trends in research

In compliance with the JTI standards
More: SWI swissinfo.ch certified by the Journalism Trust Initiative