
Rhine is river most polluted by Swiss microplastics

Every year around 15 tonnes of microplastics enter Swiss rivers and lakes. The River Rhine near Basel is the worst affected, a new model reveals.
Researchers from the Swiss Federal Laboratories for Material Science and Technology (Empa) have built a computer model to predict the concentrations of microplastics in Switzerland’s rivers and lakes.
Every year, 14,000 tonnes of plastic are discarded and end up in Swiss soils and waters, partly in the form of microplastics. These come from many sources, such as cosmetics or synthetic fibre clothing. The tiny particles are also produced by larger pieces of plastic that break down in the environment.
Of the overall amount, around 15 tonnes of microplastics enter Swiss rivers and lakes every year, Empa writes. Around half of all microplastics that enter Swiss waters remain in the Alpine country. Of that total, around one-third settles in lakes, the remainder stays in rivers.
+ Polluting particles from car tyres – how worried should we be?
However, the exact distribution of microplastics is complex, Empa says.
“A longer river does not automatically retain more particles than a shorter one. Rather, the river basin, the barrages and the lakes determine how much microplastics remains in the river and how much is transported further,” it states.
+ Switzerland has plastic problem, say most Swiss
Not surprisingly, particularly high levels of microplastics pollution can be found downstream from major cities. The Rhine near Basel contains the highest concentration of microplastics, researchers found: the river transports around 4,500 tonnes of microplastics towards Germany every year. This is also due to the River Aare, which, together with its tributaries Reuss and Limmat, drains three of Switzerland’s largest cities – Bern, Zurich and Lucerne – before flowing into the Rhine.
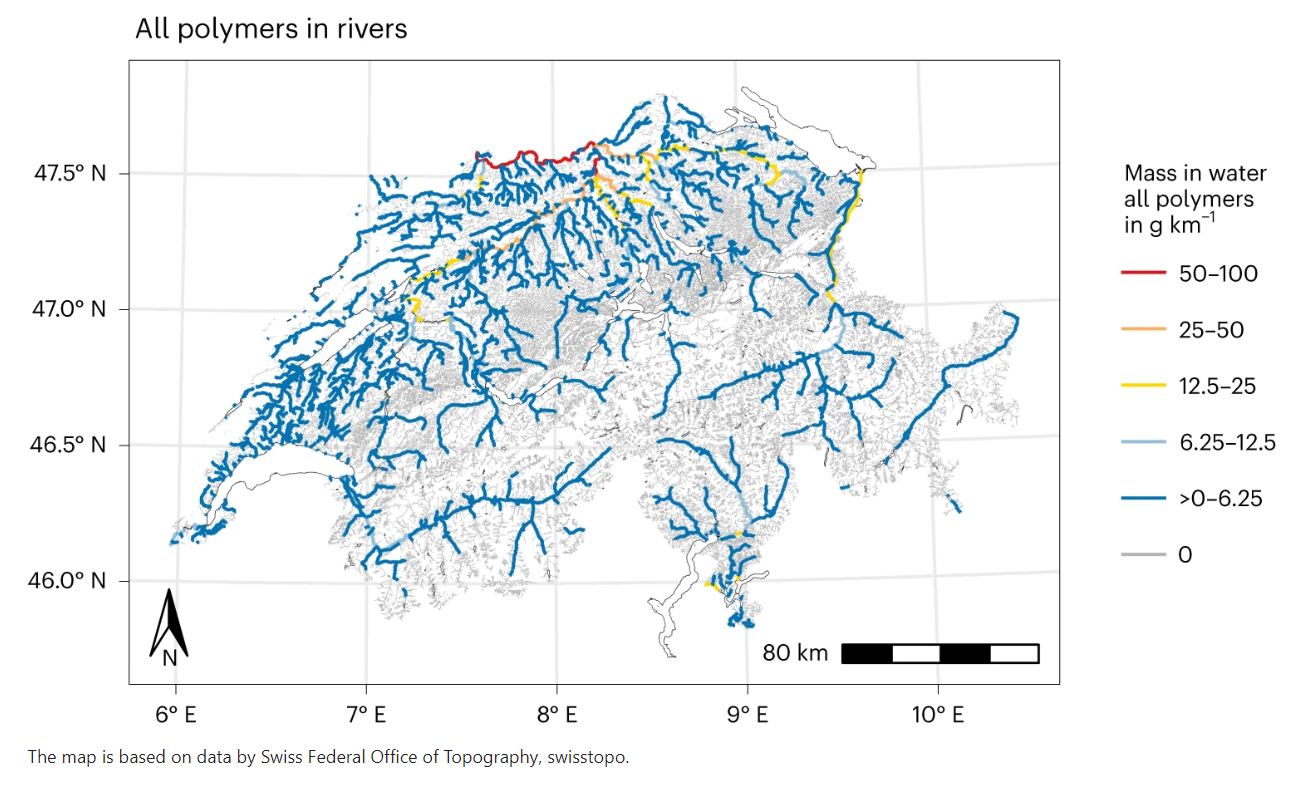
Meanwhile, 300kg per year and 61kg per year are leaving the Rhône and Doubs catchment areas, respectively, towards France. Together, these catchments cover about 88% of all microplastic outflows from Switzerland.
+ High levels of microplastic pollution recorded in Lake Lugano
The remaining 12% are shared among Lake Maggiore (6%; 327kg per year) and unknown downstream river segments: smaller border crossing rivers, 2%, the River Breggia towards Italy (2%), the River Inn towards Austria (1%) and other smaller rivers.
As a next step the Swiss researchers are developing a comparable model to predict the amount of macroplastics – such as PET bottles and plastic bags – found in bodies of water.
The scientists’ findings were published in the Nature WaterExternal link journal.

More
Is your bikini fish-friendly? Research reveals how fabrics shed microplastics

In compliance with the JTI standards
More: SWI swissinfo.ch certified by the Journalism Trust Initiative































You can find an overview of ongoing debates with our journalists here . Please join us!
If you want to start a conversation about a topic raised in this article or want to report factual errors, email us at english@swissinfo.ch.