
Diamonds from space may be from ‘lost planet’
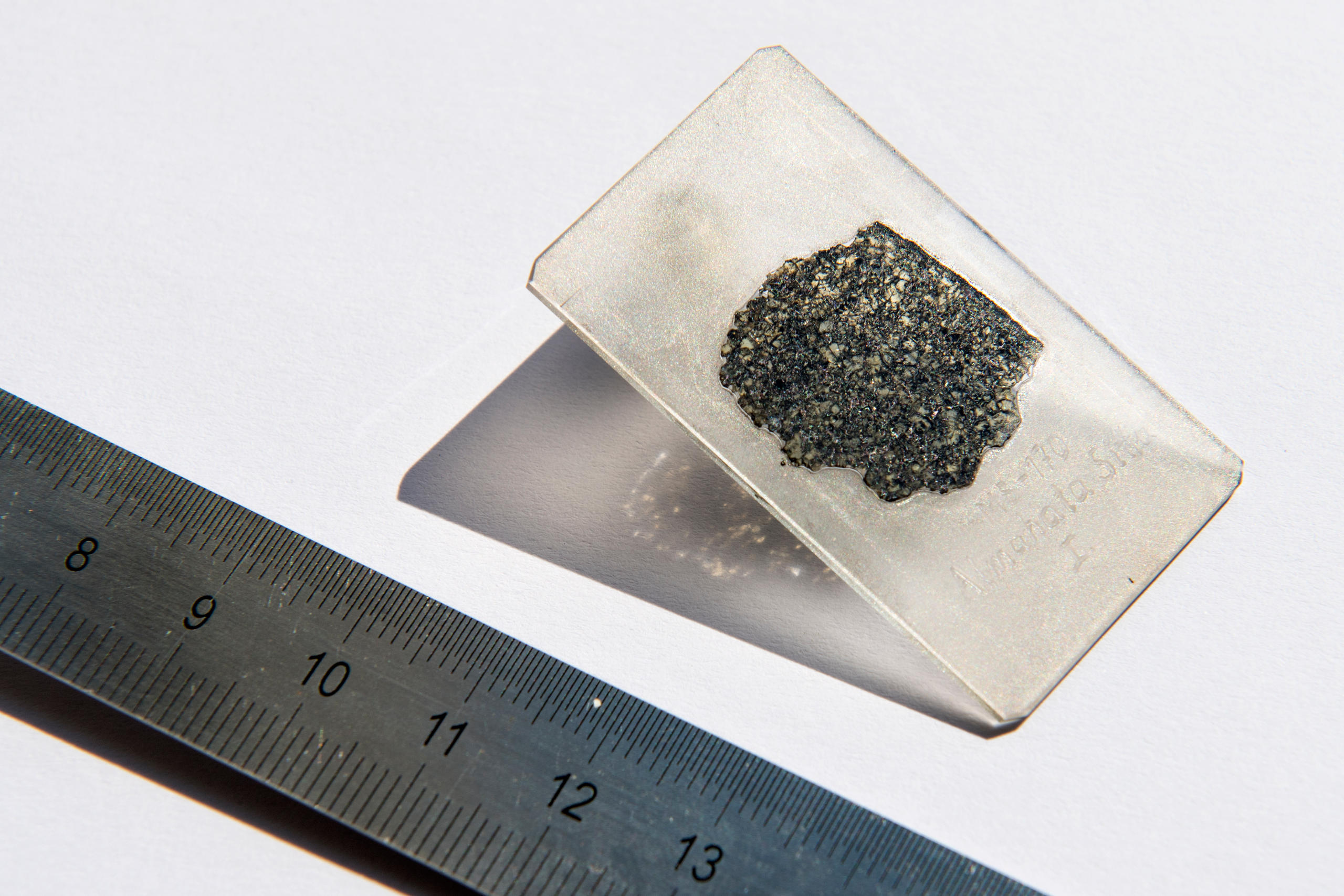
Diamonds in a meteorite that exploded over Sudan in 2008 provide compelling evidence of a ‘lost planet’ that once existed at least four billion years ago in our solar system, scientists say.
Researchers from Switzerland, France and Germany examined a slice of a so-called Almahata Sitta meteorite which exploded over Sudan’s Nubian Desert in 2008. The Almahata Sitta meteorites are mostly ureilites, a rare type of stony meteorite that often contains clusters of nano-sized diamonds.
The diamonds in the meteorite had chromite, phosphate, and iron-nickel sulfides embedded in them, known as “inclusions”, the Federal Institute of Technology (EPFL) said in a statement on TuesdayExternal link. These have been known for a long time to exist inside diamonds found on Earth, but this is the first time that they have been encountered in an extra-terrestrial body.
It is thought that these tiny diamonds can form in three ways: enormous pressure shockwaves from high-energy collisions between the meteorite “parent body” and other space objects; deposition by chemical vapor; or the “normal” static pressure inside the parent body, like most diamonds on Earth.
The research teams calculated a pressure of 200,000 bar (2.9 million psi) would be needed to form the diamonds they studied, suggesting the mystery planet was as least as big as Mercury, possibly even Mars. Their research has been published in Nature CommunicationsExternal link.
It is thought that the early solar system once contained many more planets.
“Many planetary embryos were Mars-sized bodies, such as the one that collided with Earth to give rise to the Moon. Other of these went on to form larger planets, or collided with the Sun or were ejected from the solar system altogether,” the EPFL said. “This study provides convincing evidence that the ureilite parent body was one such large ‘lost’ planet before it was destroyed by collisions some 4.5 billion years ago.”

In compliance with the JTI standards
More: SWI swissinfo.ch certified by the Journalism Trust Initiative





























You can find an overview of ongoing debates with our journalists here . Please join us!
If you want to start a conversation about a topic raised in this article or want to report factual errors, email us at english@swissinfo.ch.