
Swiss researchers develop living material from fungi
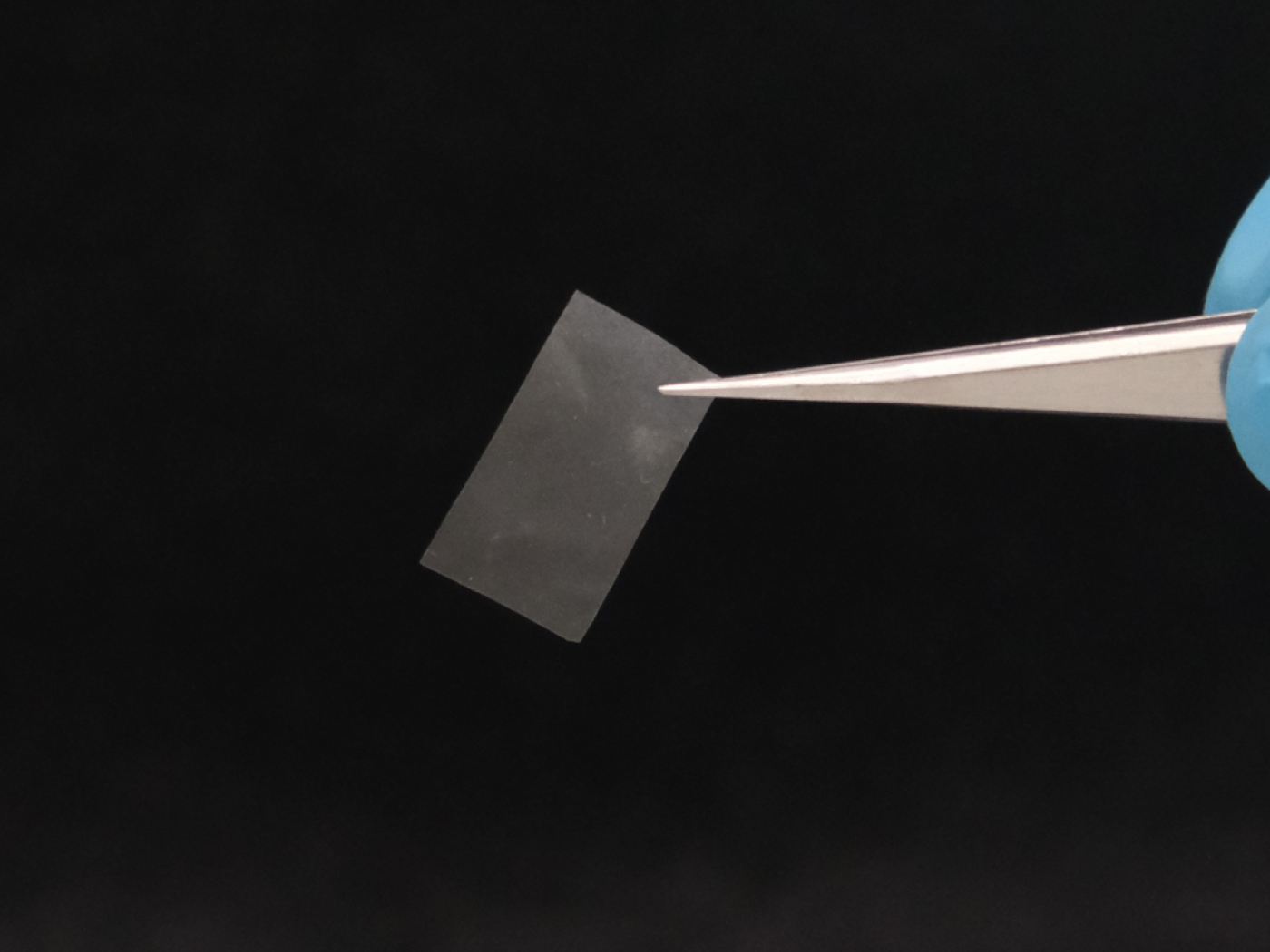
A Swiss research team has developed a new type of material from fungi. This could be used to create compostable films, moisture sensors or edible additives for food and cosmetics, they say.
+Get the most important news from Switzerland in your inbox
The secret of the new material lies in the fact that it is alive, the Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Science and Technology (EMPA) announced on Tuesday.
The researchers used the so-called mycelium of the widespread, edible fungus known as the “common split-leaf fungus” as the basis for their new material. Mycelia are root-like, thread-like fungal structures that are already being actively researched as potential material sources.
However, natural materials present a challenge: although they are biodegradable, they are often not stable or flexible enough for practical applications. To compensate for these weaknesses, they are often chemically treated, but this reduces their sustainability.
+ ‘Switzerland should be a model country for innovative sustainability solutions’
First possible applications tested
In previous tests, mycelium fibres were normally cleaned and, if necessary, chemically treated. The EMPA researchers chose a different approach. Instead of laboriously processing the mycelium, they use it as a whole.
As it grows, the fungus forms a so-called extracellular matrix: a network of different fibre-like molecules, proteins and other biological substances that the living cells secrete. The newly developed material is based on this extracellular matrix. As the material remains alive, it continues to produce the useful molecules.
In their study published in the scientific journal Advanced Materials, the researchers demonstrated initial potential applications. Among other things, they produced a plastic-like film and an emulsifier – a substance that helps to bind different liquids together in food and cosmetic products.
Translated from German by DeepL/ts
How we work
We select the most relevant news for an international audience and use automatic translation tools such as DeepL to translate them into English. A journalist then reviews the translation for clarity and accuracy before publication. Providing you with automatically translated news gives us the time to write more in-depth articles. The news stories we select have been written and carefully fact-checked by an external editorial team from news agencies such as Bloomberg or Keystone.
Did you find this explanation helpful? Please fill out the short survey below to help us understand your needs.
Don’t miss your chance to make a difference! Take our survey and share your thoughts.

In compliance with the JTI standards
More: SWI swissinfo.ch certified by the Journalism Trust Initiative






























You can find an overview of ongoing debates with our journalists here . Please join us!
If you want to start a conversation about a topic raised in this article or want to report factual errors, email us at english@swissinfo.ch.