
Parts of France and Austria put on Swiss quarantine list

Switzerland will not put its neighbours on its coronavirus high-risk list but travellers from specific regions in France and Austria will be required to quarantine themselves. Border regions will not in principle be put on the high-risk list.
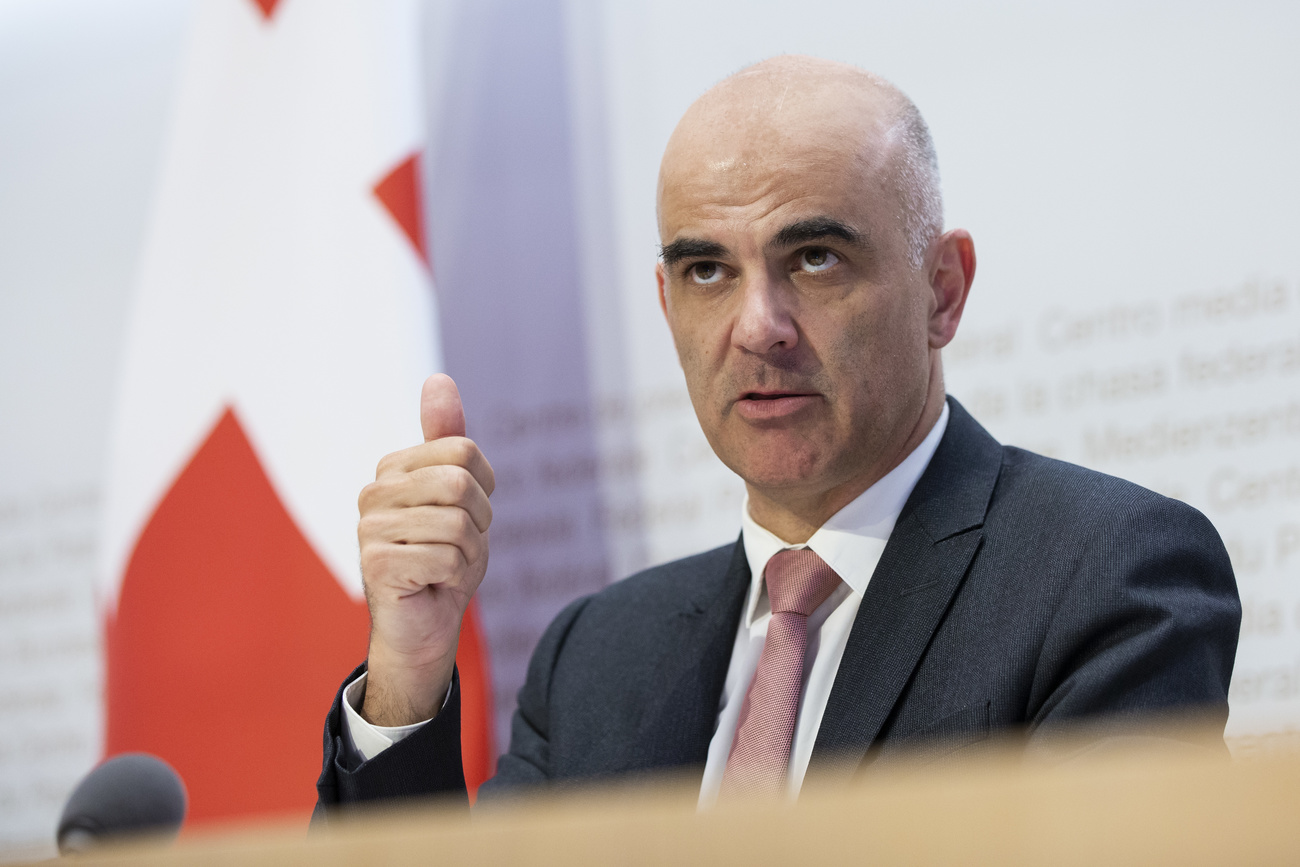
The measures will come into force from Monday September 14, Health Minister Alain Berset announced on Friday. He said one region of Austria (Vienna) and nine regions of France including Paris were being put on the high-risk list.
This means Swiss residents should refrain from going to those regions unless absolutely necessary, Berset explained. Anyone returning from there must go into quarantine for 10 days. There are some exceptions such as for medical or professional reasons.
Berset said the government had decided on a pragmatic solution because of the “intense exchange” that takes place in border regions and the number of cross-border workers in cities like Geneva and Basel. Other countries have also adopted the practice of putting regions rather than whole countries on their “red list”. Belgium, for example, has put some Swiss cantons on its list.
The minister noted that cases were rising in European countries and also in Switzerland, where the number of new daily infections has just passed 500. The new cases are mostly among people under 40, he said, while the numbers of hospitalisations and deaths are low.
He said countries were working together to keep the situation under control and maintain vital contact tracing. The situation is very different from at the beginning of the pandemic, Berset stressed, and the aim was not to close borders.
The regions of France that will be on Switzerland’s risk list from Monday are: Centre-Val de Loire, Corsica, Hauts-de-France, Île de France (the Paris region), Normandy, Nouvelle-Aquitaine, Occitanie, Pays de la Loire and Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur. There are also a number of French overseas territories (French Guyana, Guadeloupe, French Polynesia, Réunion, Martinique, Mayotte, Saint-Barthélemy and Saint-Martin).

In compliance with the JTI standards
More: SWI swissinfo.ch certified by the Journalism Trust Initiative

























You can find an overview of ongoing debates with our journalists here . Please join us!
If you want to start a conversation about a topic raised in this article or want to report factual errors, email us at english@swissinfo.ch.