
Swiss researchers make bone cancer breakthrough

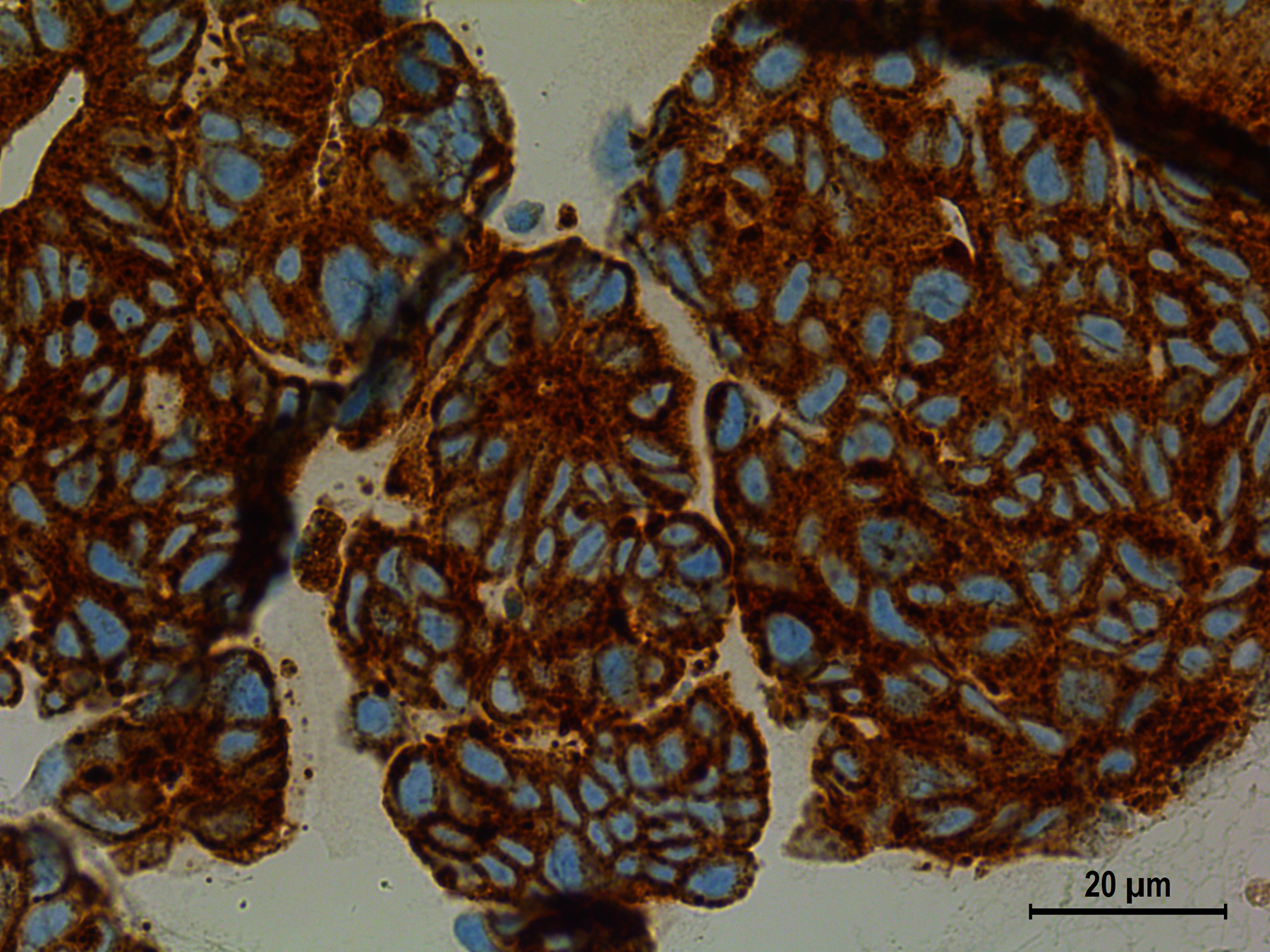
New research has enabled scientists to identify the most dangerous cancer cells found in Ewing’s sarcoma, an aggressive form of bone cancer.
Researchers from the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF) have developed a technique to identify which Ewing’s sarcoma cancer cells are most likely to trigger metastases and spread cancer within the body, the SNSF said in a statement on Wednesday.
Ewing’s sarcoma is a rare but very aggressive form of bone cancer that particularly affects children and young adults.
The scientists began by isolating the most dangerous cancer cells and growing them in a laboratory. They then genetically modified the tumour cells, introducing a gene that causes the dangerous cells to glow green if the cell is of the metastasising variety. The work has been published in the journal Science Advances.
More
Swiss-led research team uncovers key to treatment-resistant prostate cancer
“Identifying the gene associated with the risk of metastases opens new avenues for research”, said Ivan Stamenkovic, co-author of the paper and professor of experimental pathology at the University Hospital Lausanne (CHUV).
It is hoped that identifying the most dangerous cancer cells will open the door for treatments that target specific cells, Stamenkovic said.

In compliance with the JTI standards
More: SWI swissinfo.ch certified by the Journalism Trust Initiative



























You can find an overview of ongoing debates with our journalists here . Please join us!
If you want to start a conversation about a topic raised in this article or want to report factual errors, email us at english@swissinfo.ch.